Electronic Data Capture (EDC) is a vital tool in the medical research world. It is use by contract research organizations, academic researchers, Pharma companies, medical device companies, and biotech companies to gather and analyze data. As the globalization of medical research increases, electronic data capture systems are essential to keep up with the growing demands. With the cost of traditional paper-base systems rising, electronic data capture systems provide a cost-effective, compliant, and user-friendly solution.
Documentation
Electronic data capture (EDC) is a computerize system that records clinical data in an electronic format. It replaces paper-base data collection methods and speeds up time to market for drugs and medical devices. It is use widely by pharmaceutical companies, contract research organizations, and life sciences organizations. Its advantages include reduce costs and the reduce risk of reporting errors.
Electronic data capture is use in a number of EDC Clinical Trials. It can automate data collection, reporting, query resolution, randomization, validation, and more. The increasing popularity of EDC tools is driving a trend toward their widespread adoption in EDC Clinical Trials. However, despite the benefits, some trials are still using paper-based data capture methods.
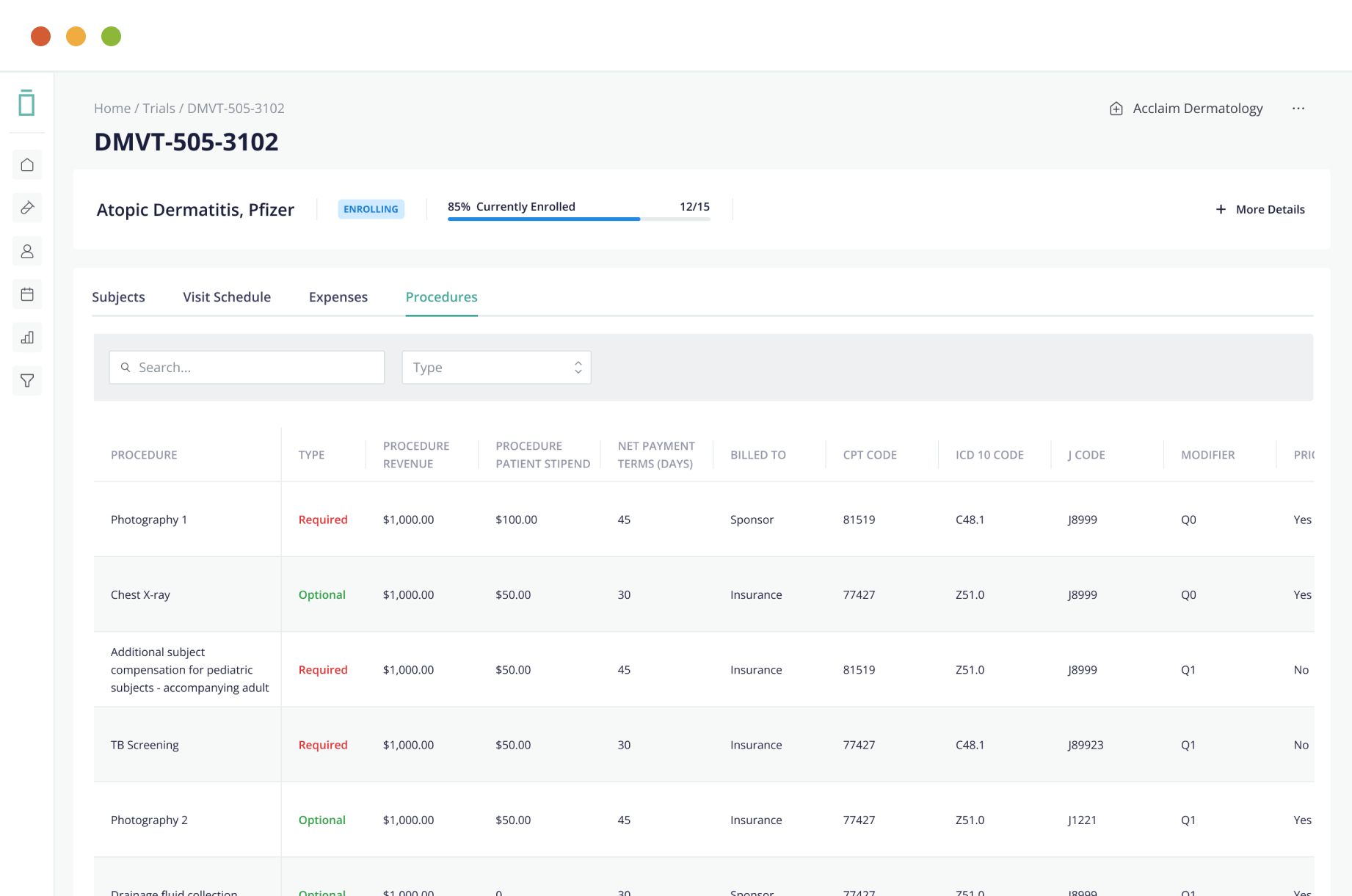
The use of an EDC system can improve the data collection process and improve data quality. It can also reduce the costs of conducting clinical studies. EDC systems can be purchase or develop by sponsors or contract research organizations, which can then implement the software. The software can also streamline data collection, storage, and management.
An EDC system must contain an audit trail that allows users to verify data integrity. A system that includes an audit trail is essential to avoid data entry errors. To ensure the safety of the data, EDC systems must be thoroughly tested to ensure that they don’t introduce any security risks. This must be a part of user acceptance testing before deployment.
Implementation of Electronic Data Capture (EDC)
The implementation of electronic data capture (EDC) is one of the key steps for improving the quality and reliability of medical research data. The use of electronic data capture systems can help reduce costs, time, and errors associate with data collection and management. In addition, EDC systems can help improve data quality by detecting missing data fields and data type violations at the time of entry.
One of the main ways to implement electronic data capture is through a web-base system know as Vial. This system was develop by a multi-institutional consortium led by Vanderbilt University. It enables questionnaire creation through an online designer or by uploading a metadata file in Microsoft Excel. It comes with an inbuilt audit trail and has the capability to integrate with other systems through web services. Vial also complies with HIPAA regulations but is not yet validate to meet 21 CFR Part 11 compliance.
Electronic data capture software helps researchers collect data from patients and other subjects. It is easy to use and allows for real-time processing. EDC software is used by many different types of organizations, including financial institutions, clinical research organizations, and sites. It can be use to collect data for complex trials or simple trials.
Clinical research and pharmaceutical development have both benefit from electronic data capture (EDC) systems. Despite the benefits, adoption of EDC systems has been slow. Regulatory requirements and economic resources have hindered its widespread adoption. Implementation is often hinder by barriers related to user motivation, user-interface interface interaction, and other factors. But there are numerous measures that can be take to minimize these challenges and ensure the success of EDC systems.
Read also: CRO Expertise in Ophthalmology Clinical Trials
Variability
Increasingly, electronic health record (EHR) systems are being implement to manage patient data. These data can be useful in clinical decision-making, transnational research, and quality evaluation of care. Researchers can analyze EHR data to identify variability in diagnostic codes and other data. An interactive web tool call the Variability Explorer Tool can help researchers visualize the variability of EHR data using an approximate probability distribution function. It can help researchers compare the variability between clinics, years, and diagnoses.
Variability can reflect real characteristics of data, such as practice-level or patient-level factors. Knowing this early on can improve research design and ensure the validity of research findings. However, it is important to remember that a single-factor model may not be the most appropriate for all research projects. Therefore, it is important to consider the etiology of data variability.
Cost of Electronic Data Capture (EDC)
Electronic data capture is an important tool in conducting EDC Clinical Trials. This technology is not only cheaper but can also provide better quality data. It can achieve up to 97% compliance rates. However, there are many factors to consider before implementing this technology. For example, the cost of electronic data capture software may not be worth it if you plan to conduct the study using paper-base forms. Another factor to consider is the learning curve associate with using this technology.
The cost of electronic data capture is often an issue for early-phase EDC Clinical Trials. This type of EDC Clinical Trials typically has a small subject population and short study duration. Many Clinical research organization are hesitant to adopt an ePRO solution, especially because of the initial set-up costs. These systems also typically require additional training for study teams.
The cost of electronic data capture software is an important consideration, but there are many ways to reduce the cost of this technology. A report will provide you with key statistics about the state of the market and help you make informed decisions. It will also provide you with an analysis of the key players in the industry. The report will also provide you with an insight into the future market for this technology.
Cost is a big factor for EDC Clinical Trials, and a software-based EDC system will streamline the process and produce higher-quality data. In addition, the software will improve data security and accessibility. As a result, the cost of an EDC Clinical Trials can be reduce.

Adoption
Electronic data capture (EDC) is a widely use administrative process in most industries. Yet, adoption rates in the research sector have been low compare to other industries. Some major barriers to EDC adoption include data security concerns, high cost, and lack of management policy. The lack of adequate technical resources may also be a hindrance. In fact, the implementation of EDC tools is a complex process. As a result, many organizations are still in the early stages of implementing these systems.
The University of Witwatersrand Faculty of Health Sciences (UWFHS) is one institution that has implemented an EDC system. Investing in an electronic data capture system signals the institution’s commitment to the end user. Moreover, a high level of reliability is crucial to establishing user trust in the system. Unreliable infrastructure is a common cause of data loss in resource-constrain settings, and users may be reluctant to use an EDC system if they fear the loss of their data. A structured training program is essential for new users to become proficient with the EDC system. Regular academic events also help promote the correct use of EDC.
The use of electronic data capture has also help speed up EDC Clinical Trials. The adoption of EDC is increasing in the industry and has been endorse by regulators. The technology has proven to be more efficient than paper questionnaires, resulting in improve participant compliance and accelerate drug development. Furthermore, users can customize trials using a web-base platform.
Healthcare organizations often use EDC to capture specific data about patients and individuals in research studies. For example, a bio-pharmaceutical organization might test a new diabetes drug in 200 subjects across 10 medical centers. Each of the medical centers uses an EDC system to enter the study data.




